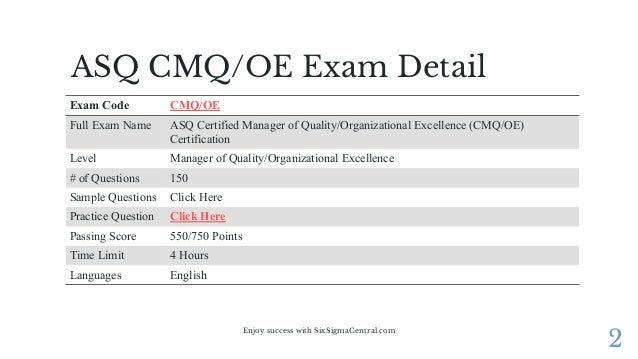
Manager of Quality & Organizational Excellence Qualification
Free CMQ/OE Practice Test
1. One impediment to contributing to effective change could be that the subjects being studied may intentionally or unintentionally change their behavior simply because they’re aware they’re being monitored, and not due to any fundamental facets of the experiment. This is what’s called the:
Hawthorne effect
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
Ramsey factor
Godfrey ambivalence scale
CMQ/OE Exam Study Guide with Practice Questions
2. The theories of Abraham Maslow are foundational portions of which of such management styles?
Scientific management
Human relations management
Management by objective
Management by results
3. The ability management approach where individuals add their knowledge with a common storehouse (say for example a database) can be described as:
Communities of practice strategy
Best practice transfer strategy
Codification strategy
Knowledge mapping strategy
4. Six Sigma has five phases (DMAIC), but it also uses many tools which are not a proprietary the main methodology. Which of such outside tools commonly used in Six Sigma would utilize an Ishikawa diagram?
TRIZ
Taguchi methods
Five Whys
Quality Function Deployment
5. The Rummler-Brache procedure for business processes is known as the:
Theory of Constraints Model
Nine Boxes Model
Interoperability Model
Seven Circles Model
Answers
1. A: Hawthorne effect. The name comes from studies of workers with a factory called Hawthorne Works in early the main twentieth century. The study found that when workers know they’re being monitored in an asq cmq oe question bank, the final results with the experiment are generally distinct from those achieved by workers getting involved in a similar experiment that are unaware actually being monitored. Sometimes the main difference is positive, and often the main difference is negative, when workers know they’re being observed in an experiment, the final results are often skewed, and this must be taken into account.
2. B: Human relations management. Abraham Maslow’s theories are foundational to the human relations management style. In Maslow’s 1954 book Motivation and Personality, he proposed that humans are motivated with a hierarchy of needs, which a lot of people have identified as a pyramid. In the bottom will be the most basic physical needs, then safety, then love/belonging, then esteem, with self-actualization at the top. Maslow believed that it’s impossible for people to achieve the objective of meeting their advanced needs if their lower level needs aren’t already being met.
3. C: Codification strategy. The ability management approach where individuals add their knowledge with a common storehouse (say for example a database) can be described as codification strategy, or push strategy. The opposite answer choices are all instruments or strategies frequently used in knowledge management.
4. C: Five Whys. An Ishikawa diagram, also referred to as a fishbone diagram, would be included in the Five Whys way of dealing with the foundation of an problem. The diagram concept was developed by Kaoru Ishikawa, which is frequently used for product design and defect prevention purposes.
5. B: Nine Boxes Model. The Rummler-Brache procedure for business processes is known as the Nine Boxes Model. It consists of three levels: Organization, Process, and Performer. Each level has three sections: Goals, Design, and Management. The Nine Boxes Model is often employed in design for employee training programs.
For details about asq cmq oe question bank take a look at this web portal: web link
